The Neuron
These specialized cells function to carry information from the brain to other parts of the body and back in order to convey orders of movement, information about pain, and other functions essential to normal life. The neuron looks like: The arrangement of neurons to each other is uniform, axon to dendrite, with small gaps in between the two cells known as a synapse.
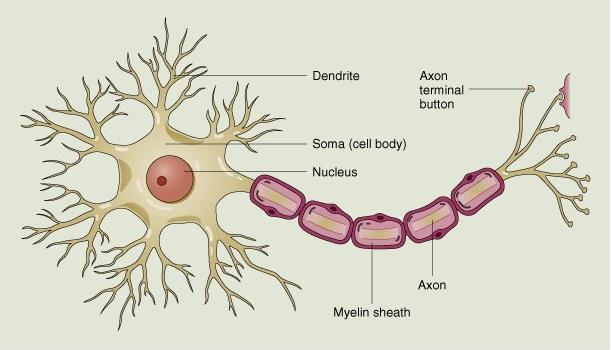
Axon- the long, tail-like structure to one end of the neuron. This recieves signals from the surrounding neurons, creating a neural pathway.
Dendrite- the branch-like structures near the nucleus, they transmit the signals outward, to the surrounding neuron's axons.
Soma Body- the main basal body of the neuron, provides the structure and functions common to all cells in a human body, and directs the neuron's signals.
Nucleus- the control center of the cell, and the location of DNA. This structure is common to all cells, and is thus not essential to the structure of the neuron.
Myelin Sheath- a form of insulation, made up of lipids. Prevents the neuron from sustaining damage from its own electric signals during the transmission of information.